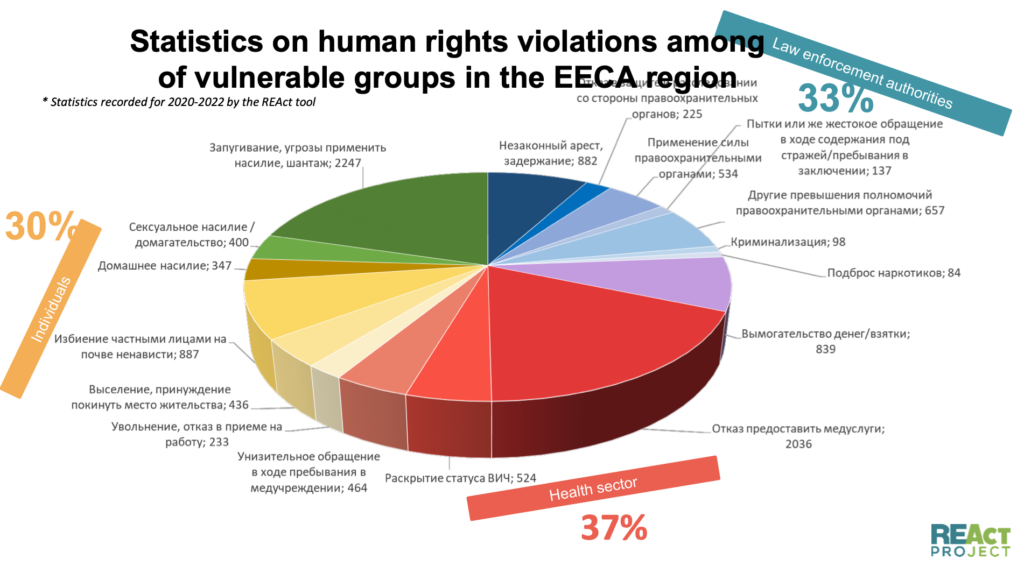
The situation of HIV-positive people in Kazakhstan faces various challenges, including discrimination and stigmatization. Despite improved awareness and access to medical care, many women continue to face limitations and challenges related to their HIV status. Consider the case of Amina (name changed), who faced discrimination and difficulties in accessing medical care for her pregnancy termination.
On March 15, Amina, who is HIV-positive, approached REActor with a question about where she should initially go to terminate her pregnancy, as she has a one-year-old HIV-positive child and is not yet ready to become a mother again. At first, the REActor referred Amina to an infectious disease doctor, which is standard practice for women with HIV, but this is where the first difficulties began. The doctor issued a certificate required for termination of pregnancy and referred her to a gynecologist at her place of residence. However, when Amina went to the polyclinic with her paid ultrasound, it turned out that the pregnancy term determined on its basis did not coincide with the results of the previous study. This led to additional tests and a delay in the procedure.
On March 27, after a repeat ultrasound and hCG analysis, she was finally given a referral to the perinatal center for termination of pregnancy. However, the maternity center denied her the operation, explaining that they could not accept an HIV-positive patient because their facility did not have a “dirty zone” for such cases. This case of discrimination was based on recent rules introduced at the perinatal center.
Fighting for rights
Rejected and humiliated, Amina went to the REActor for help. The REActor went with her to the head of the AIDS Center and found out that the rules imposed did exist. Then REActor found out that the gynecologist who treated Amina at the polyclinic knew about the new rules and should not have referred her to the perinatal center. However, the gynecologist forgot about this and gave the wrong referral, putting Amina in an even greater situation of uncertainty and anxiety.
Amina was then sent to the city hospital, but even there she was not admitted because of the wrong referral. Only after correcting the document was, she admitted to the hospital and the surgery was finally performed on April 3.
Measures against discrimination
After all, this happened, Amina decided to file a complaint against the responsible gynecologist for the wrong referral. Together with the REActor, she went to the relevant service, where her complaint was recorded. The Ministry of Health of Kazakhstan reacted quickly and took action against the doctor.
According to the Ministry’s report, the doctor was severely reprimanded, deprived of her bonus, and suspended for 6 months for advanced training. However, the doctor herself did not provide Amina with such negative experiences and discrimination.
Conclusion
Amina’s case reflects the difficulties faced by HIV-positive women in Kazakhstan, particularly in accessing health care and reproductive services. Discrimination based on HIV status remains a serious problem, and additional measures must continue to be worked on to ensure equitable access to health care.
Authorities and healthcare providers should actively work to increase awareness and education on HIV/AIDS and implement protective mechanisms to prevent discrimination based on HIV status. Such measures will help to create a more favorable and safer environment for all people, and allow everyone to receive quality health care without fear of discrimination.
Also read:
Client Incident: Wrongful Disclosure of Medical Information in Uzbekistan
Survival Story: How an organization helped a woman overcome her HIV diagnosis and start a new life